Blood Poisoning – Signs and Symptoms You Shouldn’t Ignore
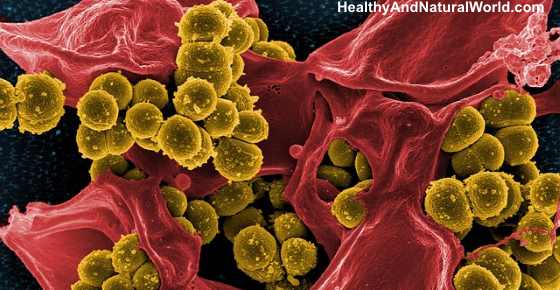
Blood poisoning (also referred to as sepsis or septicemia) is a severe infection that is spread through the body via the blood stream. If blood poisoning is left untreated it can become so severe that it starts to interfere with the body’s organs and, in the most severe cases can lead to septic shock where blood pressure falls to dangerously low levels and the organs start to shut down.
Blood poisoning can be very dangerous and it is therefore important that it is treated as soon as possible. For this reason it is vital to understand the risk factors and symptoms of this dangerous problem.
Who is at Risk for Developing Blood Poisoning (Sepsis)
Blood poisoning is rarely a problem for people who are healthy or who have a properly functioning immune system.
Those who are most at risk are the very old and the very young. Elderly people, especially those who are suffering from a chronic disease such as diabetes or heart problems may be more at risk because their immune system is not functioning at peak efficiency.
Very young babies whose immune systems have yet to develop can develop blood poisoning if they contract an infection that is not treated quickly enough. Blood poisoning can be hard to diagnose in the very young, and therefore babies with fever or other infections are often admitted to hospital for observation.
Other segments of the population may also have a heightened risk of developing blood poisoning. This includes people whose immune system doesn’t function well due to illnesses such as cancer or AIDS or those who have received chemotherapy, had an organ transplant or are recovering from a surgery (particularly if they are still in hospital), had dental extractions or who have severe open wounds.
Causes Of Blood Poisoning
Blood poisoning does not occur by itself, and is the result of the body’s reaction to another underlying infection. The causative infections are usually bacterial in nature but can sometimes be as a result of viral or fungal infections.
The most common infections that cause blood poisoning (if not treated) are urinary tract infections, pneumonia, meningitis, abdominal infection and skin infections, although it is worth being aware that any infection that is left untreated can result in blood poisoning.
Symptoms of Blood Poisoning (Sepsis)
The early symptoms of blood poisoning can be hard to identify, particularly against the background of the underlying, causative infection. The symptoms you should be aware of are:
- Most people develop a fever. Some, however, may have a normal or low temperature so do not hesitate to seek medical treatment if other symptoms are present but a fever is not present.
- Many people experience chills and may shiver or shake.
- Many people experience a fast heartbeat and some may be breathing more rapidly than normal.
If the infection has progressed to severe sepsis there are likely to be additional symptoms:
- A person will appear disoriented, agitated and confused.
- A person may have dizziness when standing.
- A person may have diarrhea and vomiting.
- The skin may be cool, moist, and usually pale.
- Some people complain of severe joint pain, back pain and abdominal pain.
- Some people also develop a rash across their body, red streaks or small red, brown, or purple spots on the skin (petechial rash). This usually indicates a spreading infection in either local blood vessels or lymphatic vessels. This rash is called
If you or anyone you know experience any combination of these symptoms, particularly if you/they are in one of the risk groups explained above, you should speak to a medical professional as soon as possible.
If it is out of hours or if you cannot contact your usual medical professional go to your nearest emergency room or call an ambulance. The sooner treatment starts the greater the chances of success.
How to Diagnose Blood Poisoning
Even if a patient shows all the symptoms listed above, it is impossible to diagnose blood poisoning without further tests.
These will typically include blood counts, blood cultures and oxygen level monitoring.
In some instances a lumbar puncture may be required.
A doctor may also order organ function tests using CT, MRI or other imaging technology.
This may seem scary and overwhelming particularly for young children and their parents but it is necessary to ensure a correct diagnosis.
Treatment for Blood Poisoning
Blood poisoning is such a serious condition that it is fatal for 40- 50% of sufferers. There is significant variation within these statistics with the most vulnerable patients (the infirm elderly and the very young) having a mortality rate of up to 80% and 5% for healthy, strong patients with no prior illnesses.
Blood poisoning is an extremely serious medical issue and has to be treated in hospital, sometimes in the intensive care unit.
The sooner a patient with blood poisoning receives medical treatment, the greater their chances of recovery. While a patient is recovering, and for some time after, they will be more vulnerable to other infections and illnesses.
Most blood poisoning patients are put on oxygen, either through a mask or a tube into the nose to help make sure that the organs are receiving enough oxygen to function.
Patients are also likely to be put on an IV saline drip to increase blood pressure and, in some situations may be given an infusion of plasma to help prevent blood clots. If a patient’s blood pressure remains low in spite of fluid treatments they may be given drugs to raise their blood pressure (these drugs are known as vasopressors) and insulin to help keep blood sugars at normal levels.
In addition to these treatments, the doctors will give the patient specific medication to control the underlying infection that has caused the blood poisoning. Often doctors will start immediate treatment with a wide spectrum antibiotic and move to a targeted treatment as soon as the cause has been identified.
How to Reduce Your Risk for Developing Blood Poisoning
Blood poisoning is an extremely scary disease but the good news is that there are precautions you can take to prevent it.
Make sure that you clean all wounds with an antiseptic solution and dress them properly to ensure that they do not get infected.
Treat all infections as soon as you notice symptoms, and if you have had surgery (medical or dental) follow all post-operative care instructions as carefully as possible and take the full course of all your prescribed medicine.
Related articles:
