Hematocrit (Hct) Blood Test: What Does Low or High Hct Levels Mean?
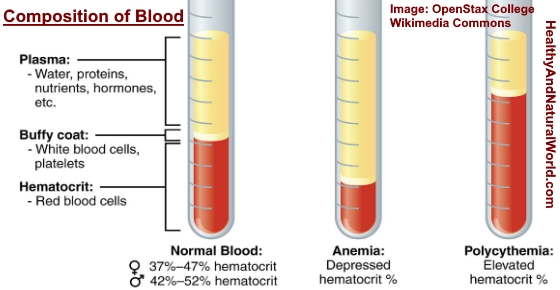
Hematocrit blood test is part of a complete blood cell count (CBC) and it measures the percentage of red blood cells (RBCs) in your blood. Results from a hematocrit (Hct) blood test can tell a doctor a lot about your general health. Usually, doctors will take into account other factors on a CBC blood test if you have low or high Hct levels.
Normal hematocrit (Hct) levels indicate that your blood has enough red blood cells to carry oxygen to your cells. Low Hct levels can show that you have anemia, a vitamin deficiency, or bleeding. A low hematocrit can make a person feel fatigued, drowsy, or have difficulty breathing.
A high hematocrit is less frequent than low hematocrit and can mean that a person isn’t getting enough oxygen, suffers from dehydration, or is at risk of heart disease. This can result in a person with high Hct levels feeling weak, dizzy, and having frequent headaches.
In this article, you will learn about the hematocrit blood test and what it can mean if you have abnormal Hct levels. Of course, if you have any abnormalities in CBC test results, your doctor will diagnose the cause and recommend a course of treatment. However, in this article, you will find out how to address some of the issues that are associated with low or high Hct levels.
What is Hematocrit?
The definition of hematocrit is the percentage of red blood cells that you have in your blood. Hematocrit readings in a CBC blood test are usually written as a percentage.
Dr. William C. Shiel on MedicineNet says that hematocrit levels can be calculated using the average volume of red blood cells and determining the amount of hemoglobin. Another way to check Hct levels is to put blood in a test tube and centrifuge it. Doctors can then measure the proportion of red blood cells at the bottom.1
A hematocrit reading of 50% (which is within the hematocrit normal range) means that 50% of the total blood volume is red blood cells.
Checking for normal hematocrit levels is one of the RBC indices that can help doctors diagnose many health conditions.
Hematocrit (HCT) vs. Hemoglobin (HGB)
When trying to understand blood test results, many wonder about the difference between hematocrit and hemoglobin.
According to the book Clinical Methods, hemoglobin is the protein found in red blood cells. Red blood cells need the protein hemoglobin to deliver oxygen to cells and tissues in the body. A lack of hemoglobin in RBCs will mean that a person will show signs and symptoms of anemia.2
Hematocrit is a calculation comparing the volume of red blood cells with the total volume of blood. Labs tests also have to take into consideration the mean corpuscular volume of your red blood cells.
Hemoglobin and hematocrit blood tests are sometimes measured together and provide similar clinical information.
Normal HCT Levels
Dr. Mandy Flannery O’Leary from the Department of Pathology at Louisiana State University explains about the hematocrit normal range. This is as follows:3
- Infants and newborns – 53-69%
- Adult males – 40-54%
- Adult females – 36-46%
For children who are ten years old, the normal Hct range is the same as that for adult females.
Depending on which lab carries out the blood tests, the results may differ slightly.
Low HCT Levels
Low Hct level is any level below the normal hematocrit range, taking into consideration age and sex.
According to Dr. Charles Patrick Davis on eMedicineHealth, there are other factors like being pregnant and living at high altitude that can affect hematocrit lab test results.4
For example, pregnant women Hct levels are classed as low if they are below 30%. Also, people living at higher altitudes are considered to have below normal hematocrit if males have less than 45% and women less than 41% red blood cell volume.
High HCT Levels (Polycythemia)
Elevated hematocrit is rarer than decreased Hct levels and is called polycythemia. High Hct levels in CBC test are readings of more than 54% for men and 46% for women.
If you are pregnant, then increased hematocrit is the same as for women who are not pregnant. However, living at high altitudes increases the normal hematocrit range to 61% for males and 56% for females. This is because there is decreased oxygen concentration in the atmosphere.
What Causes Low HCT Levels?
Let’s look in more detail at the low hematocrit causes and why lab test results for complete blood cell count can show lower than normal Hct readings.
Anemia
There are various types of anemia and reasons why a person can develop symptoms of anemia. However, low Hct levels usually show that a person is anemic, and doctors need to diagnose the reasons why not enough oxygen is being delivered in the blood.
According to the journal Critical Care Medicine, determining hematocrit and testing hemoglobin levels can help to determine how much anemic a person is. Low Hct, as well as other RBC indices, can also help to determine why the anemia has developed.5
Other symptoms of anemia can include:6
- Fatigue and general lack of energy
- Racing heartbeat or an irregular heartbeat
- Having a pale complexion
- Shortness of breath
Nutritional deficiencies
Low hematocrit can mean that you also have certain nutritional deficiencies that are connected to anemia.
The World Journal of Gastroenterology reported that low Hct can indicate a lack of folic acid and vitamin B12. This is often accompanied by an iron deficiency and a person showing the classic symptoms of anemia.7
Many people have deficiencies in B-group vitamins. This includes folic acid (vitamin B9), vitamin B6, and vitamin B12. As well as showing signs of anemia, symptoms of a B12 deficiency can also include:
- Mood swings
- Headaches
- Difficulty concentrating
- Digestive problems
- Disrupted sleep patterns
Arthritis
If you suffer from rheumatoid arthritis, you may also have low hematocrit and a lack of oxygen-rich blood cells.
The journal Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology published a study on blood test results on people with rheumatoid arthritis. It was found that low hemoglobin levels in the blood were usually associated with the severity of the disease. Low hematocrit in arthritis patients can also lead to other diseases.8
If you suffer from joint inflammation and pain because of arthritis, you should check for a vitamin D deficiency. Also, you should consume foods that help to reduce inflammation and can act as a natural remedy for arthritis.
Depression
Not having enough hematocrit can also be symptomatic of depression, increased anxiety, and panic disorder.
According to information published in the journal, Human Psychopharmacology: Clinical and Experimental, depression can increase inflammatory responses in the body. This can result in having hematocrit lower than the normal range. Researchers also found blood test results from depressed people show an increase in neutrophils and leukocytes.9
Some natural remedies to help deal with symptoms of depression include taking 5-HTP or SAM-e supplements, and psychotherapy. You can also try taking turmeric supplements because some studies have shown that turmeric can have an antidepressant effect.
Fibromyalgia
If you suffer from chronic pain associated with fibromyalgia, then lab test results may show that your hematocrit is lower than normal. Inflammation in the body affects the production of red blood cells and white blood cells.
The journal Arquivos de Neuro-Psiquiatria reported in 2016 that fibromyalgia can affect women in many ways. For example, depression and increased sexual dysfunction are some of the associated conditions with fibromyalgia. However, the study also showed that frequently fibromyalgia sufferers have lower than normal hemoglobin and hematocrit levels.10
If you are living with any kind of chronic pain, then you might find that D-Ribose supplements can help deal with the symptoms of fibromyalgia.
Kidney disease
Kidney disease can also affect the production of red blood cells and cause hematocrit to drop significantly.
A study published in 2017 in the Journal of Medical Biochemistry found that red blood cell production is controlled by hormones that are secreted by the kidneys. People with chronic kidney disease usually have lower than the normal range of hematocrit and hemoglobin.11
Your kidneys are located in the middle back and it’s important to avoid habits that damage kidney function. For example, excess sugar, smoking, overindulgence of alcohol, and a lack of exercise put extra strain on your kidneys. Drinking plenty of water is one of the best ways to keep your kidneys healthy and prevent infection.
Digestive problems
Low hematocrit can mean that you have inflammation in your digestive tract that is affecting the volume of red blood cells.
The International Archives of Allergy reported that ulcerative colitis (a form of inflammatory bowel disease) can affect hematocrit levels. It was found that people with digestive disorders and autoimmune conditions show signs and symptoms of anemia. This is often due to internal bleeding in the digestive system.12
Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis are just 2 reasons why your digestive system doesn’t work properly. Other signs of inflammatory digestive conditions include:
- Frequents bouts of diarrhea after eating
- Passing greasy stools
- Pain under your ribs
- Indigestion and heartburn
Autoimmune conditions
Low Hct is often associated with certain autoimmune conditions, and checking hematocrit levels can help doctors recommend the best course of treatment.
For example, the journal Transfusion Medicine and Hemotherapy reports that some autoimmune conditions can result in anemia.13
Low mean platelet volume (MPV) in a lab blood test can also be used to identify some autoimmune conditions.
Low Hematocrit Symptoms
Doctors often arrange for Hct test if a person complains of symptoms that are associated with low hematocrit. The reasons for a drop in Hct levels could be that red blood cells are getting destroyed quicker than the body can make them or the body isn’t creating enough of them.
Researchers from the University of Rochester Medical Center say that symptoms of low hematocrit include the following:14
- Shortness of breath
- Feelings of dizziness or lightheadedness
- Frequent headaches
- Chest pain
- Clammy skin that looks pale
What Causes High HCT Levels?
A blood test result that shows increased Hct levels could cause or be symptomatic of a number of health conditions.
Heart disease
People with inherited heart disease often have Hct levels that are above the normal range.
The Journal European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences found that taking into account hematocrit, urea, and a person’s gender can help diagnose the risk of cardiovascular diseases in some patients.14
Dr. Charles Patrick Davis says that people with congenital heart disease usually have high hematocrit.4
It’s important to take good care of your heart. Exercising regularly, eating a well-balanced diet with plenty of fruits and vegetables, and controlling stress are just some of the ways to lower your risk of a heart attack.
High blood pressure
If you suffer from high blood pressure, there is a chance that you have above normal hematocrit in CBC results.
A study in 2017 published in the Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis found that patients who have high blood pressure often had high Hct, hemoglobin, and red blood cell count values. It was also found that other RBC indices like the red cell distribution width (RDW) were also affected. The researchers suggested that hematocrit itself could show a person’s risk of hypertension.15
It’s important to keep blood pressure at safe levels to lower your risk of stroke, heart disease, and other cardiovascular problems.
Insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes
Research has shown that elevated Hct can be associated with increased insulin resistance and indicate a person’s risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
The Journal of International Medical Research found that blood tests from people with insulin resistance showed increased Hct, hemoglobin, and LDL (“bad”) cholesterol. Usually, those at risk of diabetes had a high BMI and were overweight.16
Elevated Hct can be one of the early signs of diabetes. To lower your risk of developing diabetes it’s important to be physically active to lose weight, get enough sleep, and eat foods that help control diabetes.
Metabolic syndrome
Metabolic syndrome describes a collection of conditions like high blood pressure, excess belly fat, and high cholesterol. Very often, overweight or obese persons have abnormally high hematocrit.
The journal Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome in 2018 reported that elevated hematocrit and other red blood cell indices are common in persons who show signs of metabolic syndrome.17
High Hematocrit Symptoms
Increased hematocrit means that your blood is thicker than it should be and blood won’t circulate in your body fast enough. In time, this can cause various symptoms and complications that are associated with polycythemia vera (a slow-growing blood cancer).
The National Heart, Lung, And Blood Institute say that high hematocrit symptoms can include the following:18
- General feelings of weakness and feeling dizzy
- Headaches
- An enlarged spleen that causes bloating in your upper left abdomen
- Itching all over your body after a warm shower or bath
- Bleeding from your gums
- Gouty arthritis
- Unexplained weight loss
- Excessive sweating
How Is a Low or High Hematocrit Result Treated?
To treat the symptoms of abnormal hematocrit, doctors will run more tests to diagnose exactly what the underlying cause is.4
How to Increase Hematocrit
If you show signs of low Hct and need to increase hematocrit, then there are a number of ways you can do this naturally.
It’s important to remember that the following methods are not ways to treat chronically low hematocrit, but ways to improve your cardiovascular health and address any nutritional deficiencies.
Aerobic exercising
Aerobic activity can help to increase hematocrit and reduce the symptoms of certain forms of arthritis and heart disease.
Because many factors influence hematologic indices, it can be difficult to determine exactly what influences hematocrit levels. However, according to research hematocrit increases significantly during exercise. Over time, regular exercise can normalize Hct values and also improve heart health and the cardiovascular system in general.19
For some ideas on how to regularly exercise at home to lose weight, please read my article on how to transform your body in 4 weeks and how walking can help you lose weight.
High-intensity interval training
Another way to exercise to increase red blood cell volume and raise hemoglobin levels is to do high-intensity interval training or HIIT exercises.
According to the journal Clinical Hemorheology and Microcirculation, HIIT exercising helps to increase blood fluidity and raise Hct levels. Although hematocrit returned to the pre-exercising levels about an hour after completing the exercise, high-intensity interval exercising did have a positive effect on red cell indices.20
HIIT exercises are one of the best ways to lose excess body fat quickly and help get a healthier body. You can find more information about HIIT exercises in my article on how interval training boosts weight loss and improves health.
Consuming iron-rich foods
If you have low hematocrit due to an iron deficiency, it’s important to consume foods that are naturally rich in iron. This can help to address any issues that anemia or an iron deficiency are causing.
The journal BBA Clinical reported that iron-fortified foods can help to treat symptoms of an iron deficiency. Eating foods that are naturally rich in iron or have been fortified with iron can help to increase hematocrit and hemoglobin.21
If your hematocrit is significantly lower than the normal range, your doctor may recommend iron supplements or to take B-group vitamins. Please read my article “Top Signs of Iron Deficiency and How to Increase Iron Levels In Your Blood” to find foods rich in iron and how to improve iron absorption in your body.
Flaxseed oil
Taking flaxseed oil regularly can help to increase Hct naturally if you are anemic.
According to a study published in the journal Hemodialysis International, taking 6 grams of flaxseed oil daily can have a positive effect on RBC indices. It was found that people who had anemia because of hemodialysis (kidney dialysis) showed improvement in hematocrit, hemoglobin, MCH, and MCHC values.22
Improving the health of your cardiovascular system is just one reason to eat flaxseeds every day. To get the health benefits of flaxseeds, you need to grind 3 tablespoons flaxseed into a powder just before using them. Add the powder to delicious healthy smoothies, oatmeal porridge, soups, or yogurts to help improve your health naturally.
How to Lower Hematocrit
In most cases, professional advice from a doctor and the appropriate treatment is necessary to lower elevated hematocrit levels. Usually, treatments involve reducing the thickness of blood by reducing hemoglobin levels and the number of red blood cells.
Endurance training
It has been noted that trained athletes seem to have lower Hct than the general population. A study from 2017 found that endurance training (like the type that will get you fit enough to run a marathon) can lower hematocrit and improve results in red blood cell tests that measure RBC volume.23
Read my other related articles:
- RBC Indices: What They Are and What They Tell About Your Health
- The Top 17 Foods and Herbs to Cleanse Your Blood (Research Based)
- High or Low Monocytes in Blood Test – What Does It Mean?
- Low Lymphocyte Count (Lymphocytopenia) – What Does It Mean?
Medical References
