Back and Rib Pain: Causes of Upper to Middle Back and Rib Pain
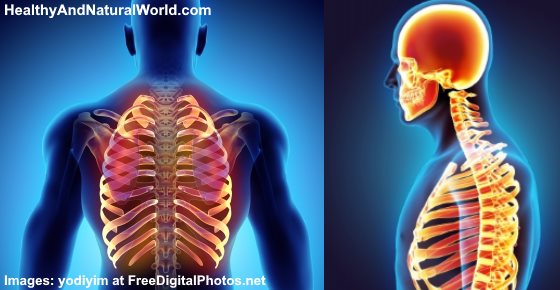
Issues with your muscles, ligaments, or ribs in your back can often cause rib pain in the back. The middle and upper part of your spine is called the thoracic region and it helps to support your upper body. Irritation, inflammation, back rib injury, strained or pulled back muscles, or a herniated disc can all cause pain in ribs and back.
Back rib pain or middle back pain is less common than lower back pain. However, pain in your upper or middle back can cause a lot of discomfort in your day-to-day activities. Depending on the cause of mid-back pain, you may have dull aches and discomfort between your shoulder blades. Sometimes, the back pain can feel as sharp and jabbing discomfort that suddenly gets worse. Or, back muscle stiffness may make lifting your arms sore and painful.
There are many ways to get rid of back and rib pain without having to turn to painkillers. For example, hot or cold compresses can help to increase blood circulation and speed up the healing process. Or, you may have to improve your posture to ease nagging pain and prevent rib pain in your middle back. In many cases, stretching exercises strengthen and flex the strained muscles and ligaments in your middle back to relieve pain.
In this article, I will examine what medical research says about the causes of back and rib pain. Knowing what can affect your rib cage, back muscles, and ligaments that support the spine can help to take steps to relieve the pain.
Anatomy of the Upper Back and Middle Back (Thoracic Spine)
Your upper and middle back starts from just below your neck and extends to about 5 inches below your shoulder blades.
Your thoracic spine gives your upper body strength and stability and helps you lift heavy objects. Your rib cage also protects many vital organs like your heart, kidneys, and lungs. According to Dr. William Blahd on WebMD, vertebrae in your middle back attach to your ribs which wrap around to your chest and are attached to your sternum.1
You have discs in between the vertebrae in your spine to absorb shocks and prevent the bones rubbing together. Also, many muscles between your ribs called intercostal muscles provide strength to your upper body and assist in breathing. There are also many nerve fibers that are attached to your spinal column.
An injury to the ligaments, ribs, nerves, or muscles in your middle back can affect your back and also radiate to other areas of your body. For example, back rib damage could also cause pain that wraps around your ribs to the front of your chest and breastbone. Or, the pain may radiate to your shoulder blade, neck, or even abdomen.
General Causes of Upper and Middle Back Pain (Thoracic Back Pain)
In many cases, the reasons for experiencing thoracic back pain are connected with your ribs and connecting tissue. However, inflammation of the organs in your upper chest or heart-related pain may feel like rib pain in your upper and middle back.
Dr. William Blahd on WebMD says that some of the general causes of upper and middle back pain include:1
- Overuse injuries from overstretching your back muscles and ligaments
- Injury to your rib cage, intercostal muscles, or ligaments in your thoracic back
- Damage to any of the discs between your spinal vertebrae
- Breakdown of cartilage caused by degenerative bone conditions
- Infections to organs in your upper abdominal and chest areas
Symptoms of Back and Rib Pain
Because upper and middle back pain can have a number of causes, there are also many accompanying symptoms to back and rib pain. Some of the symptoms of back rib pain include:
- Sharp or jabbing pain in the middle back due to a strained or pulled muscle
- Bruising and swelling around the injured area on your back
- Middle back pain that worsens when stretching, coughing, or breathing deeply
- Dull aching discomfort to the left or right of your spine
- Tense back muscles and painful muscle spasms
- Pain that radiates from the back and wraps around the rib cage
- Tingling down one or both arms
Causes of Back Pain and Rib Pain
Let’s look in more detail at the various causes of pain in the ribs and back.
Intercostal muscle strain
Twisting your upper body or suffering blunt trauma to your back can strain the intercostal muscles in your rib cage. The injury can result in a pulled muscle, torn muscle, or muscle strain that results in sharp, intense jabbing pains in your middle back
Intercostal muscle strains commonly affect athletes, manual laborers, and office workers who sit for long periods of time. According to the Journal of Physical Therapy Science, overstretching the intercostal muscles can cause chronic or acute middle back pain because it puts pressure on the rib cage. This can result in upper thoracic pain that may or may not radiate to other parts of the body. In some cases, the mid-back pain can come on suddenly as a result of an injury.2
Doctors from the Mayo Clinic say that other symptoms of muscle strain that could affect your thoracic area include:3
- Swelling around the affected area
- Pain and discomfort when moving your upper body
- Muscle spasms in your middle or upper back
Doctors recommend stretching exercises to strengthen the intercostal muscles and reduce middle and upper back pain. This helps the improve stability in the upper body, improve breathing, and increase chest expansion.
Intercostal neuralgia
Damage to the nerves in your rib cage can result in inflammation and pain in your thoracic region that wraps around to your chest.
Nerve damage in your thoracic area can be caused by wear and tear, aging, trauma, herpes zoster virus (shingles), or surgery to your back. The Journal of Neurology & Translational Neuroscience reports that intercostal nerves supply sensation to the ribs, muscles, and skin of the back. Intercostal nerve damage can cause sharp pains to spread the length of the nerve and result in shoulder blade pain, back pain, and upper thigh pain. This can also result in the following symptoms:4
- Muscle twitching and spasms in your back, shoulder, or arm
- Tightness in the upper and middle back
- Loss of sensitivity in some areas of the body due to intercostal nerve damage
Doctors say that some complications of intercostal neuralgia can include a frozen shoulder, chronic middle back pain, left or right side chest pain, disruption to sleep patterns, and decreased appetite.
Because intercostal neuralgia can cause both thoracic pain and chest pain, it’s important to visit your doctor if you suffer tightness and left-sided pain in your chest. This is one of the signs of an impending heart attack, so unexplained chest pain should never be ignored.
Costochondritis
Costochondritis is inflammation of the joints between your breastbone and rib cage and often causes left-sided chest and back pain. The burning sharp pain can often occur below your left shoulder blade and become a source of chronic back pain.
According to Dr. William Shiel on eMedicineHealth, costochondritis usually causes pain in your chest. However, the pain often radiates from the front of your chest, wrapping itself around your rib cage to the middle back. The discomfort can feel like sharp aching pains that get worse when you sneeze or cough.5
At the end of this article, you will find out how to use heat or cold compresses to get rid of costochondritis back and chest pain that affects your ribs.
Poor posture
Poor posture can put an extra strain on the ribs in your back, increase back tension, and cause upper back pain and discomfort.
According to research carried out in the journal Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research, poor posture can cause pressed or trapped nerves in your upper spine. This can lead to irritation and pain in your upper or middle back.6
Also, the journal Public Health Reports found that poor posture whilst sitting in front of a computer can lead to backache. It was found that individuals who used a computer often, were at greater risk of neck and upper back pain than those who don’t sit at desks for a long time.7
Arthritis
Arthritis that affects your thoracic area can be a source of chronic and constant upper to middle back pain. Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis can cause inflammation of the vertebrae in your spine. In some cases, a breakdown of the joint tissue can aggravate the already painful symptoms of a sore upper back.
The journal Nature Reviews Rheumatology reported that osteoarthritis of the spinal joints is a common source of thoracic back pain. The pain can get worse when you extend your lower back area or rotate your upper body. The area where the joint inflammation occurs may also be tender to touch.8
According to research published in the journal BMJ, arthritis can cause stiffness and pain in the upper back that makes it difficult to bend forward or backward. The pain from the middle back may radiate to the neck and cause pain between the shoulder blades.9
Problems with spinal discs
A herniated, ruptured, or slipped disc in the spine can cause middle back pain when moving your upper body. The back pain may feel worse when twisting or bending at the waist and may cause neck pain.
The Journal of Manual and Manipulative Therapy found that injuries to the discs in the cervical spine (in the neck area) can cause pain that spreads to the upper thoracic spine. The type of pain in the thoracic area caused by spinal issues is described as severe, intense, debilitating back pain. These injuries can affect nerves that can also cause headaches and other neurological problems.10
Researchers from the University of Maryland report that a herniated thoracic disc can cause intense sharp pain that happens suddenly. However, you may have a herniated disc without back pain. This can happen if the ruptured disc presses on a spinal nerve and this can result in any of the following symptoms:11
- Muscle weakness
- Numbness in one or both legs
- Pain that travels through your body
According to a report in the journal International Surgery, a thoracic disc herniation can also cause chronic abdominal pain. The researchers suggested that it is possible to mistake symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome for thoracic pain that radiates from the middle back.12
Injury to ribs
Of course, any injury to your upper or middle back can cause varying degrees of thoracic pain. The injury to your back ribs could result in dull aching sensation in your middle back to sharp intense pain that makes moving difficult.
Injury to your rib cage could also damage your kidneys which are located in your middle back behind your ribs.
Myofascial pain syndrome
A feeling of knots and pain in your middle back could be a symptom of myofascial pain syndrome. Myofascial pain is pain in the muscles and can affect your intercostal muscles between your ribs. This can result in areas of your rib cage that are tender to touch and reduced mobility in your back.
According to the American Association of Occupational Health Nurses, myofascial pain syndrome can cause painful rib syndrome.13 Some of the symptoms of painful rib syndrome can include:14
- Sharp stabbing pains that become dull aches in the thoracic region
- Pain that wraps around your ribs from your chest to middle back
- Pain that gets worse when bending over, coughing, or breathing deeply
- Upper abdominal pain
- You may also have sleeping difficulties
- Intercostal neuralgia
Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia is a chronic painful condition that can cause back and rib pain. According to Dr. Carol DerSarkissian on WebMD, fibromyalgia often causes pain that feels like it comes from the ribs in the upper back, neck, chest, rib cage, or lower back.15
Some other symptoms of fibromyalgia include:
- Tender muscles and tendons when pressed
- Tender points in the back, shoulder, hip, and elbow
- Sleeping difficulty
- Irritable bowel syndrome
If you suffer from chronic pain, then you should find out about the best foods to help manage chronic pain.
Other Causes of Middle Back Pain and Rib Pain due to Internal Organs
There are other, potentially serious, causes of rib pain and middle back pain that may seem to originate from the back ribs but are actually caused by issues with your internal organs.
Gallstones
Gallstones are small buildups of cholesterol that can form in your gallbladder and cause right-sided pain under your rib cage. Doctors from WebMD say that gallstones can cause sharp sudden pains under your right ribs that may spread to your right shoulder. A gallbladder attack can also cause upper abdominal pain along with nausea and vomiting.16
Pleurisy
Pleurisy is painful inflammation of the lining of the lungs and inner chest wall which can cause varying degrees of pain. Dr. George Schiffman on MedicineNet says that if the back part of the lung is affected, you may have middle back or shoulder pain. The pain will feel worse with deep breaths and you may have sharp back pains when you cough.17
Collapsed lung
A collapsed lung is another pulmonary issue that can cause sharp pains in your middle back that feels as if you have sore ribs. According to Dr. John Cunha on eMedicineHealth, a collapsed lung (pneumothorax) can cause chest pain below your ribs that radiates to your thoracic region in your back.18
Kidney stones
Kidney stones can cause excruciating pain below your ribs under your breast. Doctors from the Mayo Clinic say that a kidney stone usually causes pain when it moves in your urinary tract. This can cause flank pain, middle back pain, and pain that spreads to your groin.19
You can drink apple cider vinegar to get rid of kidney stones quickly and naturally.
How to Treat Middle Back Pain and Rib Pain
There are many ways that you can treat rib pain and middle back pain that originates from inflamed or strained muscles. Here are some of the best natural remedies for back rib pain.
Heat or ice treatment
Warm compresses or cold compresses can help to quickly relieve pain in your rib cage caused by injuries, inflammation, or other painful causes.
According to researchers from the University of Rochester Medical Center, a cold pack or compress can help to reduce pain, swelling, and inflammation in the first 48 hours after an injury. After that time, you should use a warm compress to increase circulation and reduce muscle spasms and stiffness.20
To make a warm or cold compress to treat rib pain in your middle or upper back, this is what you should do:
Cold compress for injuries to your middle back
- Take a bag of frozen peas or place crushed ice in a sealable plastic bag and cover with a thin towel.
- Lie on your front and place the ice pack on your middle or upper back.
- Leave for 15-20 minutes.
- Repeat every hour to help reduce swelling and muscles strain in the first two days after an injury.
Warm compress for back rib pain
- Fill a hot water bottle with hot, but not boiling water, and cover with a towel.
- Place the hot water bottle under the sore area in your middle back and lie on it for 15 to 20 minutes to help reduce the pain and ease muscle stiffness.
- Repeat 2-3 times a day for best results and continue using until your back pain has gone.
Hot and cold compresses are also excellent natural remedies for relieving lower back pain.
Rest
Rest is important for relieving any kind of muscle or ligament strain to your intercostal muscles in your back. This helps to prevent further injury, and together with hot and cold packs should help to speed up recovery.
However, too much rest may not be good to help muscle strains and tears to repair themselves. The European Spine Journal reported that too much bed rest could actually aggravate back pain. It was found that bed rest for 3 days for acute back pain was just as effective as resting for 7 days. The goal of resting should be to return to normal activities as soon as possible and have a regime to strengthen the back muscles.21
Improve posture
If you suffer from chronic rib pain in the middle of your back, you should try to improve your posture to relieve pressure and tension from your rib cage.
The Journal of Physical Therapy and Science reported that improving your posture is an effective treatment method for mid-back pain, shoulder pain, and low back pain. This includes learning how to sit at a desk properly and stand properly.22
Please read my article on effective exercises to get rid of back pain with proper posture for the best advice on how to improve your posture.
Stretches to Improve Back Pain and Rib Pain
Stretching your back can help to lessen rib pain and improve the symptoms of middle back pain.
According to the International Journal of Sports Physical Therapy, muscle stretching is one of the best ways to manage back pain, lessen muscular tension, and increase muscle strength. This provides better support for your upper body and increases the range of pain-free motion.23
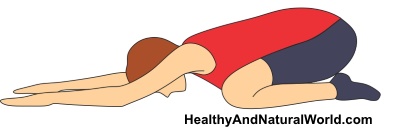
The prayer stretch (similar to the child’s pose in yoga poses) can help to relieve irritation of the joints and ligaments in your thoracic region. (If you have herniated thoracic discs, you should seek medical advice before attempting this exercise). This is what you should do:
- Sit on your knees so that your buttocks are resting on your heels.
- Put your hands on the floor and slowly extend them forward as far as you can.
- Keep moving your hands forward, keeping your buttocks on your heels, until you can almost touch the floor with your nose.
- Hold for 30 seconds to help stretch your spine and relieve middle back pain.
- Repeat 2-3 times and do every day to help increase strength and flexibility in your back.
Exercises to Treat Back Rib Pain and Middle Back Pain
Apart from stretching, there are many effective exercises that can help to prevent rib pain in your thoracic area and upper back.
The Journal of Physical Therapy Science reported on the effect of exercises to reduce thoracic pain. It was found that exercising strengthens the muscles and ligaments in the upper back and is an effective way to manage lower and middle back pain.24
You can use a foam roller to help mobilize your upper back and improve mid-back strength and. This is what you should do:
- Lie on the foam roller so that it is directly under your middle back. (The roller should be perpendicular to your back).
- Lift your hips off the ground and place your hands behind your back to support your head.
- Tighten your glutes.
- Use your legs to slowly roll from mid-back to your upper back.
- Roll back to the starting position with the foam roller under your middle back.
- Repeat a few times to mobilize your upper and middle back.
Remember, that you shouldn’t roll your neck or lower back with this exercise.
When to See a Doctor for Rib Pain and Middle Back Pain
In most cases, your upper rib cage pain in your back should go away with simple stretching exercises and back-strengthening exercises. However, in some cases of chronic middle back pain and rib pain, you should see a doctor.
According to the National Institutes of Health, you may need professional medical attention in the following circumstances:
- You have middle back pain or lower back pain that causes tingling in your legs or arms.
- You have severe back pain that wraps around your ribs that doesn’t go away.
- The middle back pain persists after an injury or fall and home treatment doesn’t help relieve the pain.
- You notice any changes in your bladder or bowel function along with back pain.
- You have any kind of unexplained chest pain.
Read my other related articles:
- Left or Right Side Chest Pain: 27 Causes You Should Never Ignore
- Pain Under Ribs: The Most Common Causes and Treatments
- Seven Types of Pain You should Never Ignore
- Intercostal Muscle Strain: Causes, Symptoms and Treatments
Medical Sources